The Great Depression: Unraveling the Causes
The Great Depression, also known as the biggest stock market crash in history, was a cataclysmic event that had far-reaching consequences. It was triggered by a combination of factors, including economic imbalances, speculative excesses, and policy failures.
One of the key causes of the Great Depression was the rampant speculation in the stock market, driven by the belief that stock prices would continue to rise indefinitely. This led to an unsustainable bubble, which eventually burst on October 29, 1929, famously known as Black Tuesday.
However, the stock market crash alone cannot be solely blamed for the Great Depression. Other factors, such as the unequal distribution of wealth, overproduction in industries, and a decline in international trade, also played significant roles in exacerbating the crisis.
The Duration and Widespread Impact
The Great Depression lasted for approximately a decade, from 1929 to the late 1930s. It was a period marked by widespread unemployment, bank failures, and a severe contraction in economic activity.
The impact of the Great Depression was felt not only in the United States but also across the globe. The economic downturn spread to other countries, leading to a worldwide recession. Nations heavily reliant on international trade suffered immensely as demand for goods and services plummeted.
Human Tragedies and Legal Consequences
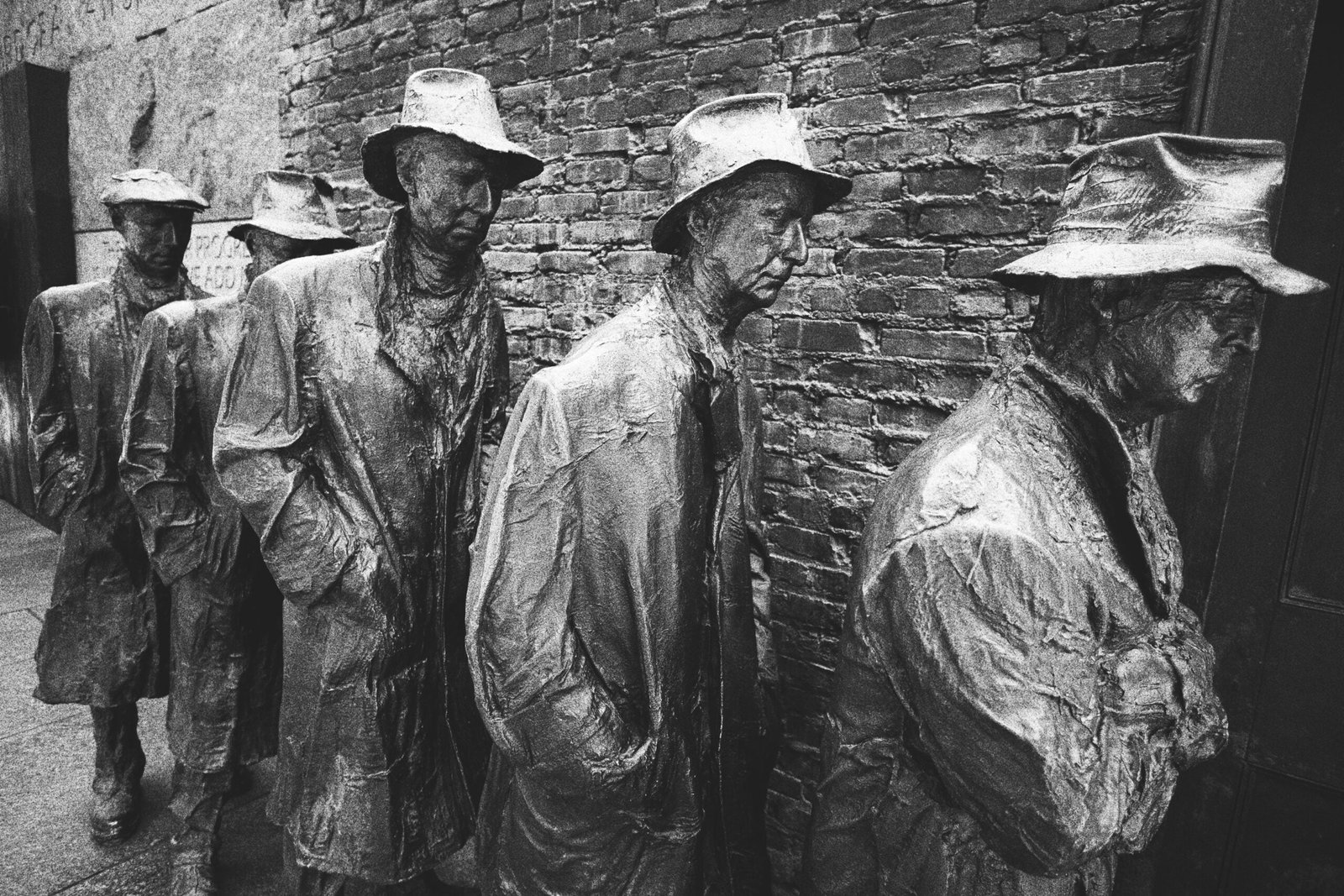
The Great Depression resulted in immense human suffering. Unemployment rates soared, and millions of people lost their jobs, homes, and life savings. Poverty, homelessness, and hunger became widespread, leaving families and communities devastated.
While the Great Depression did lead to a surge in suicides, it is important to note that the majority of suicides during this time were not caused by individuals jumping out of buildings, as popularly depicted. The economic hardships and despair experienced by many individuals, however, did contribute to an increase in suicide rates.
In terms of legal consequences, some individuals were indeed jailed for fraud and other financial crimes related to the stock market crash. Notable cases include the prosecution of several high-profile financiers and executives involved in fraudulent practices.
The Lasting Effects and Lessons Learned
The Great Depression had a profound impact on the world, shaping economic policies and perceptions for decades to come. Governments around the world recognized the need for regulation and oversight to prevent such a catastrophic event from happening again.
In the United States, the Great Depression led to the implementation of various reforms, including the establishment of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the creation of social safety net programs, such as Social Security. These measures aimed to prevent future stock market crashes and mitigate the impact of economic downturns on vulnerable populations.
The Most Affected and Lessons Learned
The Great Depression affected people from all walks of life, but certain groups were particularly vulnerable. Unskilled workers, farmers, and minorities, including African Americans and Hispanics, faced disproportionate hardships during this period.
Lessons learned from the Great Depression continue to shape economic policies to this day. The importance of maintaining stable financial markets, reducing income inequality, and implementing social safety nets are just a few of the enduring lessons that emerged from this devastating period in history.
In conclusion, the Great Depression was a complex and multi-faceted event that had far-reaching consequences. It was caused by a combination of factors, including the stock market crash, economic imbalances, and policy failures. The impact of the Great Depression was felt globally, leading to widespread human suffering and significant legal consequences. However, it also resulted in lasting changes and lessons learned, shaping economic policies and perceptions for generations to come.